The next assumption states that the weighted average of common shares outstanding is 1.4bn. For companies seeking to increase their book value of equity per share (BVPS), profitable reinvestments can lead to more cash. In return, the accumulation of earnings could be used to reduce liabilities, which leads to higher book value of equity (and BVPS). If we assume the company has preferred equity of $3mm and a weighted average share count of 4mm, the BVPS is $3.00 (calculated as $15mm less $3mm, divided by 4mm shares). If a company’s share price falls below its BVPS, a corporate raider could make a risk-free profit by buying the company and liquidating it. If book value is negative, where a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, this is known as a balance sheet insolvency.
Correlation between Book Value per Share and Market Value per Share
Conceptually, book value per share is similar to net worth, meaning it is assets minus debt, and may be looked at as though what would occur if operations were to cease. One must consider that the balance sheet may not reflect with certain accuracy, what would actually occur if a company did sell all of their assets. This formula shows the net asset value available to common shareholders, excluding any preferred equity. Nevertheless, most companies with expectations to grow and produce profits in the future will have a book value of equity per share lower than their current publicly traded market share price. Although infrequent, many value investors will see a book value of equity per share below the market share price as a “buy” signal. But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong.
What Is Book Value Per Common Share?

Over time, the historical cost basis may not reflect the true worth of assets due to inflation, depreciation, and changes in market conditions, leading to potential misvaluation of the company’s stock. BVPS is significant for investors because it offers a snapshot of a company’s net asset value per share. By analyzing BVPS, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, aiding in the assessment of whether a stock is over or undervalued. Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share.
Book Value: Meaning, Formula, Calculation and Examples
However, success in the modern business world is frequently linked to a company’s intangible assets including brand recognition, patents, copyrights, and company reputation. These valuable resources aren’t reflected on the balance sheet and do not contribute to the BVPS. These include the exclusion of intangible assets’ value, the impact of inflation, potential inaccuracies due to accounting methods, and the exclusion of future growth potential.
To put it simply, this calculates a company’s per-share total assets less total liabilities. The book value per share (BVPS) metric helps investors gauge whether a stock price is undervalued income taxes by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. BVPS is what shareholders receive if the firm is liquidated, all tangible assets are sold, and all liabilities are paid.
- BVPS is found by dividing equity available to common shareholders by the number of outstanding shares.
- In other words, it is calculated by taking the original cost of the asset and subtracting the accumulated depreciation or amortization up to the current date.
- Book value per share holds a significant relationship to a company’s commitment to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and sustainability.
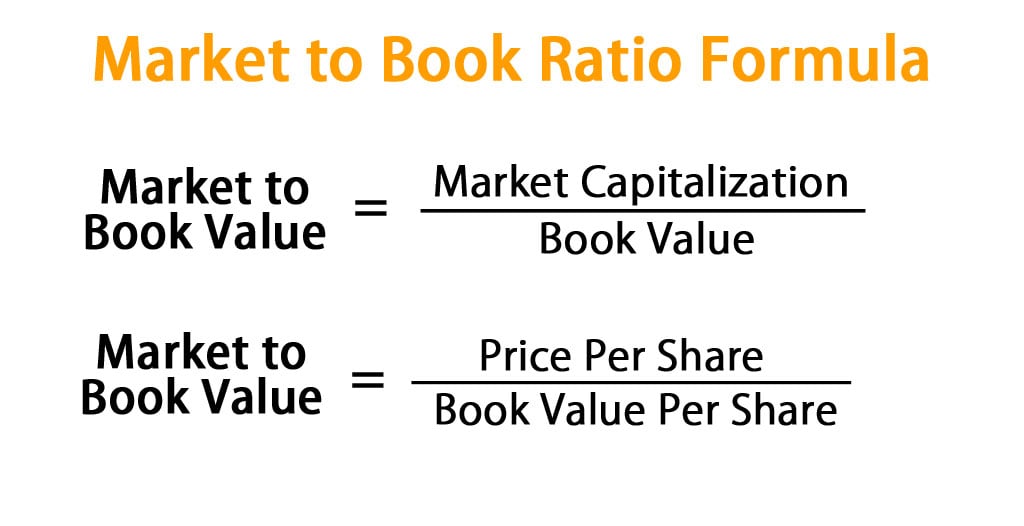
- A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value.
- In conclusion, book value per share can hold meaningful implications for a company’s commitment to CSR and sustainability.
Using the same share basis formula, we can calculate the book value per share of Company B. Book value per share is just one of the methods for comparison in valuing of a company. Enterprise value, or firm value, market value, market capitalization, and other methods may be used in different circumstances or compared to one another for contrast. For example, enterprise value would look at the market value of the company’s equity plus its debt, whereas book value per share only looks at the equity on the balance sheet.
For instance, banks or high-tech software companies often have very little tangible assets relative to their intellectual property and human capital (labor force). Now, let’s say that XYZ Company has total equity of $500,000 and 2,000,000 shares outstanding. In this case, each share of stock would be worth $0.50 if the company got liquidated. To calculate book value per share, simply divide a company’s total common equity by the number of shares outstanding.
It is essential to differentiate between book value per share and market value per share. While book value per share represents the company’s net asset value, market value per share reflects the current market price at which the shares are being traded. Now, let’s say that Company B has $8 million in stockholders’ equity and 1,000,000 outstanding shares.
Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments. There are other factors that you need to take into consideration before making an investment. However, book value per share can be a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments. BVPS is more relevant for asset-heavy companies, such as manufacturing firms, where physical assets constitute a significant portion of the balance sheet. BVPS is typically calculated quarterly or annually, coinciding with the company’s financial reporting periods.
To better comprehend the book value per share, let’s examine its components, which include tangible assets, intangible assets, and liabilities. A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value. For value investors, this may signal a good buy since the market price generally carries some premium over book value. There is a difference between outstanding and issued shares, but some companies might refer to outstanding common shares as issued shares in their reports.
